Trees
Linked lists and array-based lists work well for representing linear relationships, but not all relationships are linear. In this chapter, we are going to investigate one of the most nonlinear data structures: trees.
As the name implies, it looks like a tree, containing roots, branches, and leaves. In trees, items are organized in hierarchical way, with some nodes being "above" and some "below" others.
A tree is a general and natural model to describe the world. Just to name a few:
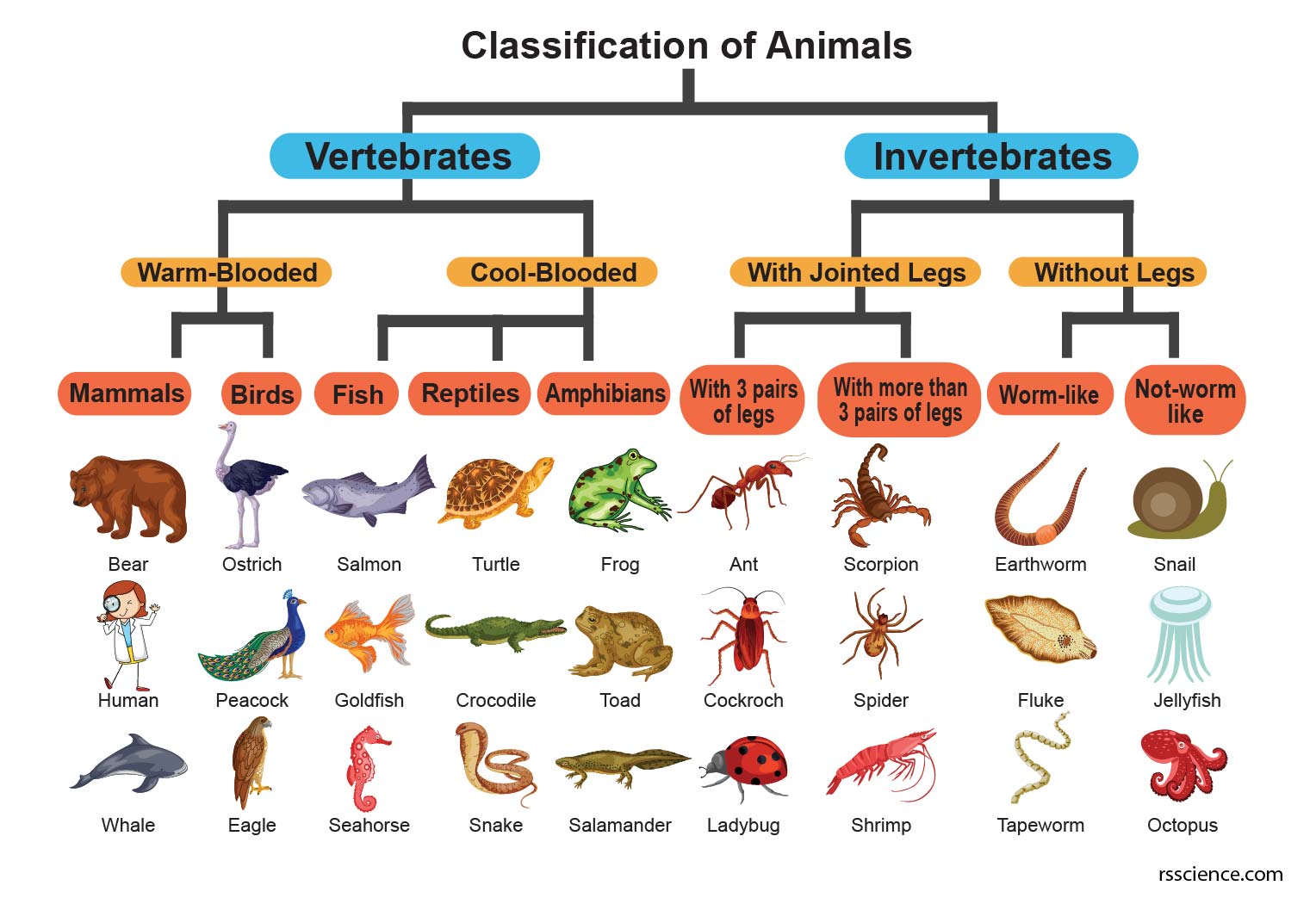
- Animals can be classified into 2 main groups: vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates can even classified into warm-blooded and cool-blooded, while invertebrates can classified into: with jointed legs and without legs.
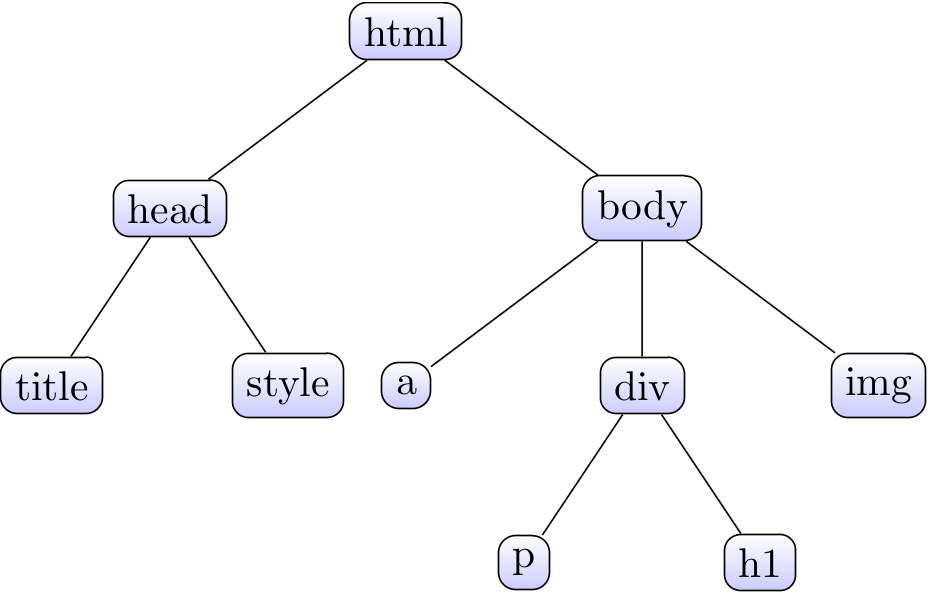
- HTML can be nested. For example,
<html>is the root tag, and it has two major nested elements:<head>and<body>. Inside the head, typical elements include<title>and<style>; while inside the body, typical elements include<h1>,<p>.