Chapter 7: Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf is a modern server-side Java template engine for both web and standalone environments. It as a better alternative for JSP. In Chapter 5, we have introduced how to use scriptless JSP. But JSP has an obvious pitfall: we cannot preview it. In contrast, Thymeleaf is featured for its natural templates. To be specific, HTML that can be correctly displayed in browsers and also work as static prototypes, allowing for stronger collaboration in development teams.
Like JSP and other template engines, Thymeleaf does the work at the server-side. So, the projects which wish to separate front-end and back-end completely, modern front-end frameworks (e.g., Vue and React) are preferred.
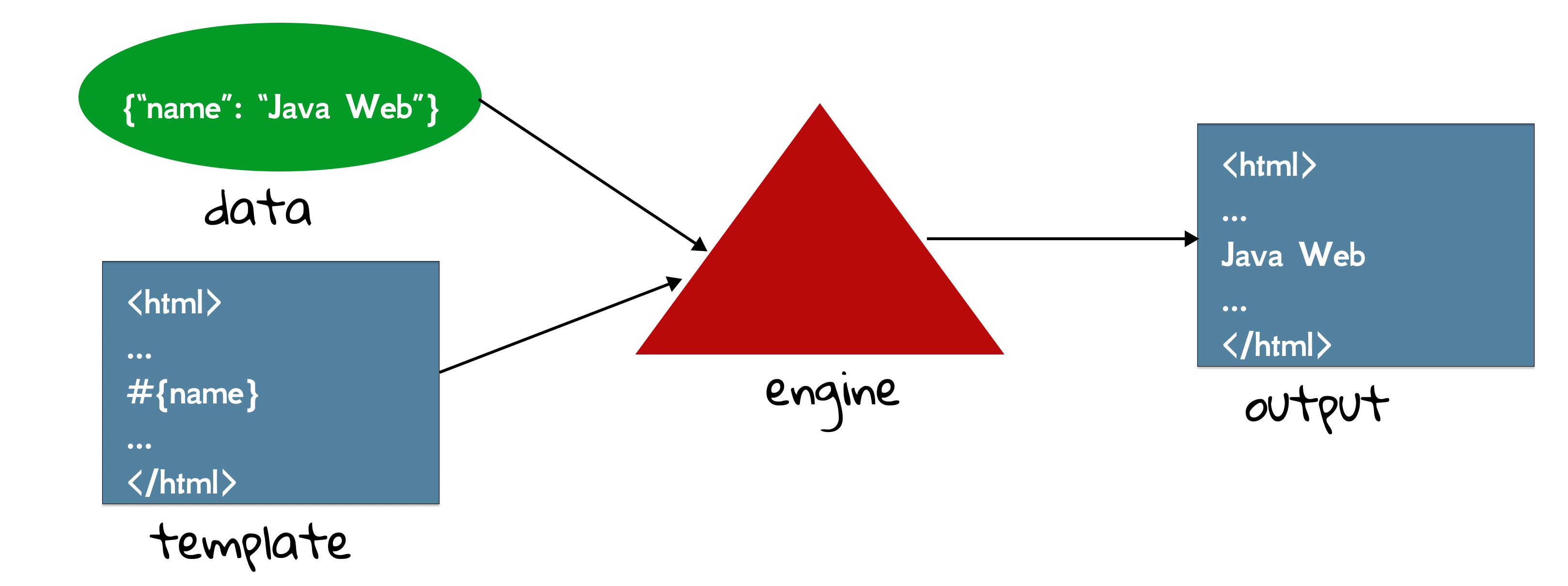
In this chapter, we focus on how to Thymeleaf in Java web. Note that the knowledge of JSP is not in vain, because essentially, all template engines work similarly, as shown in Fig 7.1. It takes the data and template as the input, and output the HTML to the client[1]. You can think of it as format() method. The string with a placeholder I am learning %s is the template, and name is the data.
String name = "Java Web";
String result = String.format("I am learning %s", name);
[1] Thymeleaf allows you to process six kinds of templates, including HTML, XML, TEXT, JAVASCRIPT, CSS and RAW.